이 논문은 hourglass network 구조를 파악하기 위해 보았고, 자세히 분석하지는 않았습니다.
Single-Image Depth Perception in the Wild
Weifeng Chen, Zhao Fu, Dawei Yang, Jia Deng
[Submitted on 13 Apr 2016 (v1), last revised 6 Jan 2017 (this version, v2)]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.03901
Single-Image Depth Perception in the Wild
This paper studies single-image depth perception in the wild, i.e., recovering depth from a single image taken in unconstrained settings. We introduce a new dataset "Depth in the Wild" consisting of images in the wild annotated with relative depth between
arxiv.org
Abstract

-
a new dataset “Depth in the Wild”(DIW) consisting of images in the wild annotated with relative depth between pairs of random points
-
a new algorithm that learns to estimate metric depth using annotations of relative depth
이 논문의 장점은 단순화했다는 것이다.
* 참고로 Zoran의 알고리즘인, 이미지 전체 pixel의 관계를 파악하여 depth를 추정하는 것보다는 부정확함
Introduction
기존 데이터셋의 한계 : range, resolution이 다양하지 못하고, transparent object에는 실패한다.
* images in the wild의 ground truth 모으는 것이 불가능하다.
* 절대적 depth 차이는 not unique (착시현상에 때문에)
* 인간이 metric depth and values를 알아내는 것은 unclear
=> annotations of relative depth만을 이용하여 metric depth를 추정하는 것은 학습이 가능
* relative depth의 annotations만으로 depth를 추정하도록 2가지의 접근방법이 있다.
* a multi-scale deep network that produces pixel-wise prediction of metric depth
* a loss function using relative depth
Related work

* 기존 RGB-D Datasets과 차이점: our dataset covers a much wider variety of scenes* 기존 Intrinsic Images in the Wild과 차이점: we sample random points instead of centers of superpixels & we sample only one pair of points per image instead of many to maximize the value of human annotations
* 기존 Zoran 알고리즘과 차이점: per-pixel metric depth를 직접 예측하는 end-to-end로 학습된 single deep network임. 따라서, ordinal relations의 중간 분류가 없어서 inconsistencies를 해결하는 데 필요한 optimization이 필요 없음
* 기존 Learning with Ordinal Relations과 차이점: pixel-wise, simple, 출력 resolution이 입력 resolution과 같음
Datatset construction
1) 이미지: Flickr에서 다운 받음. random query keywords이용하여 골고루 다운 받음
=> 그림, 인공 이미지 제거
2) workers에게 point 1,2 중에 가까운 곳을 고르도록 질문
* How Many Pairs? one per image (=querying only one pair per image)
(to maximize the amount of information)
* Which Pairs? 50퍼는 unconstrained pairs(아래부분일 수록, 센터일수록 가까워 보이는 착시현상 존재), 50퍼는 symmetric pairs(센터에서 정확히 좌우로 uniformly 떨어진 두 쌍)

* Protocol and Results? gold-standard images와 비교해 정확도가 85퍼 아래이면 버림. 두 workers에게 each query(an image and a point pair)을 주고 둘 다 동일하다고 말하면 데이터셋에 업로드함. 그렇지 않으면 버림. è gold-standard images와 비교해 1%미만의 오답을 가진 dataset완성
* 1.24M이미지 중 0.5M의 유효한 답을 얻음. (261K는 unconstrained pair 240K는 symmetric pairs)
Learning with relative depth
** Zoran의 방법 - centers of superpixels사이의 첫번째 관계를 예측하는 classifier을 학습시킴. 그 다음 energy minimization을 이용하여 depth를 만듬. 그 다음 per-pixel depth를 만들기 위한 각 superpixel을 채움.)
** 우리의 방법 - 어떠한 image-to-depth 알고리즘도 이미지를 pixel-wise depth로 mapping하는 함수를 계산해야만 한다는 것을 이용.
=> input과 output이 같은 resolution을 가진 네트워크 & annotations of relative depth로 훈련시키는 네트워크 !! 이 두가지를 만족하는 network를 design
* Network Design: 입력 이미지와 출력 이미지가 같은 resolution을 가진 네트워크 è hourglass network를 수정하여 사용. (inception module도 수정하여 사용)

* Loss Function: only ordinal annotations를 사용하는 네트워크를 훈련시키기 위해 사용
ground-truth ordinal relations를 가진 depth map 예측을 위한 loss function 필요
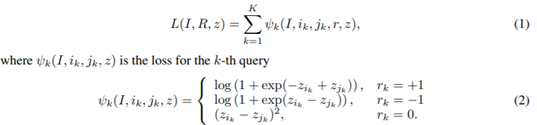
* Novelty of Our Approach: 우리의 것은 Pixel-wise prediction과 ranking loss를 동시에 수행한 첫번째 알고리즘이라는 것에 의의가 있음
Experiments on NYU Depth
: indoor scenes with ground-truth Kinect depth


본문에서 만든 Dataset

=> 네트워크 구조를 파악하기 위해 분석한 논문이라 5, 6번의 자세한 내용은 생략하겠다.
Conclusions
제한되지 않은 설정에서 찍은 단일 이미지에서 depth를 회복하며 wild 단일 이미지 깊이 인식을 연구했다. 상대적인 깊이로 주석을 단 wild 이미지로 구성된 새로운 데이터 세트를 도입하고 상대적인 깊이에 의해 감독되는 metric 깊이를 추정하는 방법을 학습하는 새로운 알고리즘을 제안했다. 기존 RGB-D 데이터 및 새로운 상대적 깊이 주석과 결합하여 우리의 알고리즘이 선행기술과 알고리즘을 능가한다는 것을 보여주었으며, 이는 wild 단일 이미지 깊이 인식을 상당히 개선시켜 준다.
'인턴일지' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [2주차] 주간프레젠테이션 (0) | 2020.05.11 |
|---|---|
| [1주차] 주간프레젠테이션 (0) | 2020.05.11 |
| Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation (0) | 2020.05.08 |
| Revisiting Single Image Depth Estimation 논문 정리 (1) | 2020.05.08 |
| Semantic Segmentation 강의 정리 (0) | 2020.05.08 |



